
Feeding

• What type of feed should farmer choose for culturing fish?
A key consideration in reaching good management and making better decisions is understanding the feed ratio or feed conversion ratio (FCR) in the production.
• Feed is the highest cost among production costs.
• Therefore, aquaculture farmers need to understand the feed factor well because the cost of production even if some of the feed is not eaten by the fish or some fish are lost during the farming process, all feed is still a cost in production.
• Formula for calculating feed conversion ratio (Feed Conversion Ratio "FCR")
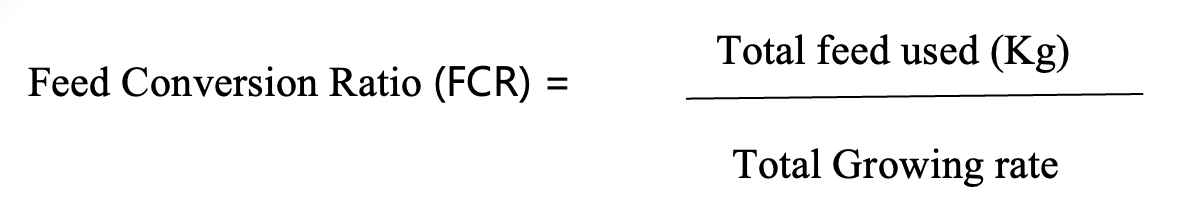
• Example: Calculating Feed Conversion Ratio
- Number of fingerling 5000
- Average weight of fish is 5 grams
- Total weight of fish when first stocked: 25 kg (5000 fish x 5 grams)
- Total weight at harvest: 2125 kg
- Total weight growing of fish 2100 kg.
- Total weight of feed used in the production (pellet feed) 3500 kg.
- Feed conversion ratio (FCR) 3500 ÷ 2100 = 1.67
- Feed conversion ratio (FCR) of 1.67 is good data for culturing, but farmers must compare it to the price of feed pellets used to know the quality of the feed.
• The feed evaluation method is: Feed cost x Feed conversion ratio (FCR)
• For example, farming for 4 months yields an average fish weight of 0.5 kg/head.
• Feed FCR greater than 1.67 but fish are not growing well (0.3-0.4 kg/head), meaning that feed quality is poor and should be changed to a new type of feed with better quality.
• If FCR is greater than 1.67 (possibly up to 2), but the average fish weight gained (0.5 kg/head) is in line with the plan, this data means that the use of excess feed is technically incorrect.
• A feed coefficient smaller than 1.67 means that the fish are not growing well (0.2-0.3 kg/head), meaning that the feed is of poor quality or that the feed is not being fed adequately.
• FCR smaller than 1.67 means that the fish grow quickly (weighing more than 0.5 kg/head), meaning that the feed is good quality and sufficient.
• Therefore, aquaculture farmers need to check the quality of feed and control the feeding method.
• The FCR is large or small depending on a number of factors as follows:
Fingerling stocked
Feed used (high or low protein level)
Feeding method (management)
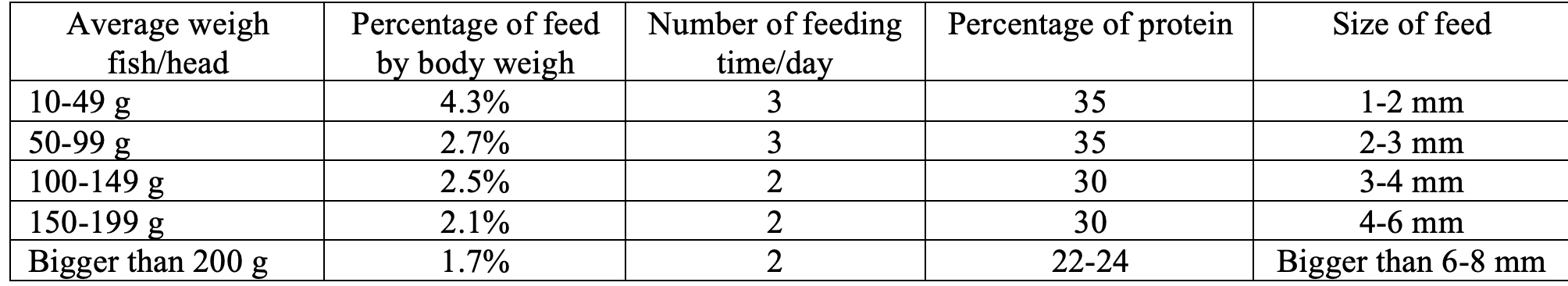
• Feeding: Determining the amount of feed, protein level, feed size, and feeding time are important factors for fish to grow faster and achieve planned yields.
• The daily amount of feed to be given to fish must be studied and calculated clearly.
• Feeding methods and daily feed calculations include the following:
Technical table of fish feeding (for pelleted feed/finished feed) ÷
• How to calculate the daily feed requirement÷
Example: A pond stocking 10,000 fingerling, with an average fish weight of approximately 82 grams/head.
How much food should a farmer feed per day?
If the total average weight of fish in the pond = 82 grams x 10,000 fish = 820,000 grams or = 820 kilograms
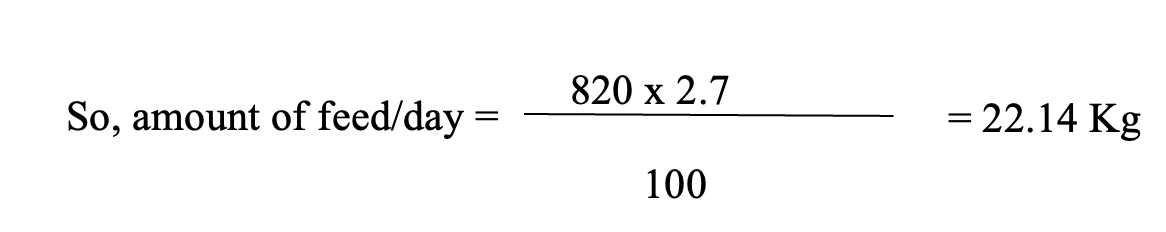
• According to FCR and feed calculations according to the fish farming technical documents of the CAST project
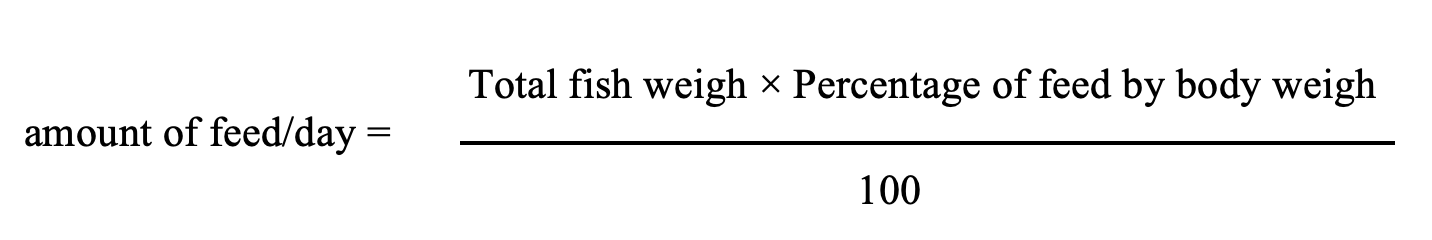
Total fish weigh = Average weigh fish/head x Total number of fish in pond